Edge-LB provides layer-7 inbound load balancing and proxying through the Edge-LB API server and Edge-LB pools. This section provides a deeper view into the details of the Edge-LB architecture and how it works.
The following diagram provides a more detailed representation of the Edge-LB architecture.
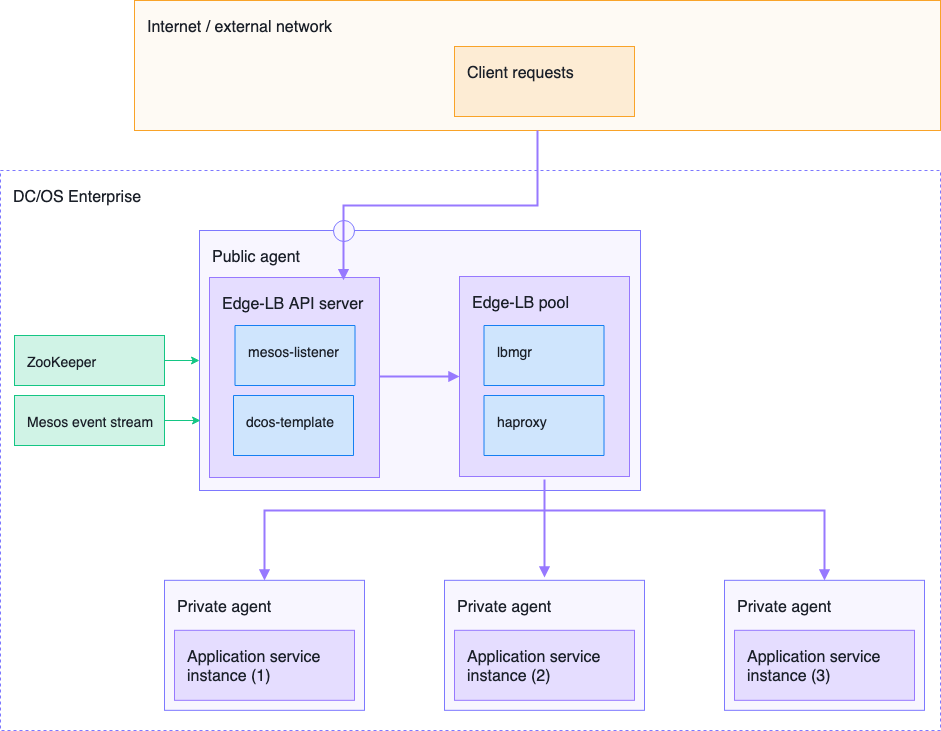
A closer look at the Edge-LB API server
The Edge-LB API receives incoming client requests and, based on the action requested, creates, deletes, or updates Edge-LB pool instances. The API server also serves API endpoint requests for Edge-LB pool(s) instances.
The Edge-LB API server uses the DC/OS ZooKeeper persistent storage to store the configuration file for the load balancer and communicates to the Edge-LB pool instances through ZooKeeper™ transactions. The interaction between ZooKeeper and the Edge-LB API server enables Edge-LB to be fault tolerant. In the event of an API server failure, the Edge-LB pool instances continue to load-balance traffic to the proper backend. When the Edge-LB API server comes back online, it re-establishes the communication between itself and the pool instances.
The Edge-LB API server has two sub-components:
- Apache® Mesos® listener
- DC/OS template
Mesos listener
The mesos-listener sub-component is always up by default. It subscribes to the Mesos event stream, translates the event stream data into an internal data structure, and serves metadata from the data structure through the API server. It also runs a gRPC server to serve the Mesos task information to other Edge-LB components like dcos-template and cloud controller.
DC/OS template
The dcos-template sub-component dynamically renders the load balancer configuration information for HAProxy® by combining the mesos-listener output and the Edge-LB pool configuration provided by the Edge-LB CLI client. The template then signals the lbmgr sub-component to take appropriate action on the HAProxy load balancer instance.
In the event of Edge-LB pool update, the dcos-template re-generates the HAProxy load balancer configuration from the Edge-LB pool configuration file and signals lbmgr to reload the existing HAProxy configuration in real-time.
A closer look at Edge-LB pools
The Edge-LB pool provides the core load balancing functionality for Edge-LB software. Edge-LB automatically provisions pools using pool templates. A default pool template is created at the time of Edge-LB installation.
To create a pool instance, you must define configuration settings in a pool configuration file. You can set up load balancing for one service or for multiple services using the same pool configuration file, depending on your application and network requirements.
Edge-LB pool has two sub-components:
- Load balancing manager (lbmgr)
- HAProxy
Load balancing manager (lbmgr)
The load balancing manager (lbmgr) in Edge-LB pool instances is a non-distributed process that runs along with the HAProxy load balancer on an agent. lbmgr takes the appropriate action for the pool when it receives requests from the API server.
The lbmgr component monitors the HAProxy instances for the Edge-LB pool and restarts HAProxy in a single container, when needed. If an HAProxy instance goes down because an agent is disconnected, the SDK scheduler restarts the HAProxy instance on another available agent.
The lbmgr component also validates new HAProxy configuration settings and reloads HAProxy load balancer instances, when necessary. For example, the lbmgr component manages the timeout interval for reloading the HAProxy instance.
HAProxy instances
Individual HAProxy instances provide the proxying and load balancing functionality for Edge-LB to the proper backend services.
 Edge Lb Documentation
Edge Lb Documentation