These sample exercises demonstrate exposing and accessing the NGINX™ service by using both Marathon-LB and Edge-LB. It demonstrates the differences in configuration in terms of both load balancers.
Before you begin
You must have:
- The Edge-LB API server installed as described in the Edge-LB installation instructions.
- The DC/OS command-line interface (CLI) installed and configured to communicate with the DC/OS™ cluster.
- The
edgelbcommand-line interface (CLI) installed. - An active and properly-configured DC/OS Enterprise cluster with at least one DC/OS private agent node to run the load-balanced service and at least one DC/OS public agent node for exposing the load-balanced service.
- Marathon-LB installed as described in the Marathon-LB installation instructions.
Preview of what you’ll do
This tutorial illustrates the differences between configuring load balancing using Marathon-LB and an Edge-LB pool to provide public access to a simple Marathon app. In this tutorial, you will:
- Create and deploy a sample Marathon app called
nginx. - Configure and deploy Marathon-LB using the Marathon service
nginx-mlb. - Configure and deploy load balancing using the Edge-LB pool instance called
nginx-edgelb. - Access the sample
nginxapp through the public agent URL.
Configure the sample app for Marathon-LB
These steps illustrate how you can configure and deploy the nginx service through Marathon-LB.
-
Copy and paste the following sample app definition into your text editor to create the
nginx-mlb.jsonfile:{ "id": "/nginx-mlb", "cpus": 0.1, "instances": 1, "mem": 128, "cmd": "sed -i 's:Welcome to nginx!:Welcome to nginx! - through Marathon-LB:g' /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html; nginx -g 'daemon off;'", "container": { "portMappings": [ { "containerPort": 80, "protocol": "tcp", "servicePort": 10020 } ], "type": "MESOS", "docker": { "image": "nginx" } }, "networks": [ { "mode": "container/bridge" } ], "labels": { "HAPROXY_GROUP": "external", "HAPROXY_0_STICKY": "true", "HAPROXY_0_VHOST": "<Public agent IP address>" } }This sample app definition includes the public IP address used to expose and access the
nginxservice. -
Deploy the
nginxservice by adding thenginx-mlb.jsonapp definition to the cluster:dcos marathon app add nginx-mlb.json -
Verify access to the service by opening a web browser and navigating to the public agent IP address and service port defined in the
nginx-mlb.jsonfile.http://<Public agent IP address>:10020
Configure the sample app for Edge-LB
These steps illustrate how you can configure and deploy the nginx service through Edge-LB.
-
Copy and paste the following sample app definition in your text editor to create the
nginx.jsonfile:{ "id": "/nginx", "cpus": 0.1, "instances": 1, "mem": 128, "cmd": "sed -i 's:Welcome to nginx!:Welcome to nginx! - through Edge-LB:g' /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html; nginx -g 'daemon off;'", "container": { "portMappings": [ { "containerPort": 80, "protocol": "tcp", "name": "nginx-port" } ], "type": "MESOS", "docker": { "image": "nginx" } }, "networks": [ { "mode": "container/bridge" } ] } -
Deploy the
nginxapp:dcos marathon app add nginx.json -
Copy and paste the following in your text editor to create the
nginx-edgelb.jsonpool configuration file to expose and access thenginxservice:{ "apiVersion": "V2", "name": "nginx-edgelb", "count": 1, "haproxy": { "frontends": [ { "bindPort": 15001, "protocol": "HTTP", "linkBackend": { "defaultBackend": "nginx-backend" } } ], "backends": [ { "name": "nginx-backend", "protocol": "HTTP", "services": [ { "marathon": { "serviceID": "/nginx" }, "endpoint": { "portName": "nginx-port" } } ] } ], "stats": { "bindPort": 1025 } } } -
Deploy the Edge-LB pool configuration file to expose and access the
nginxservice:dcos edgelb create nginx-edgelb.json
Verify deployment status for sample apps
-
Verify that the Marathon-LB and Edge-LB API server packages deployed successfully:
dcos package list -
Verify the services and pool instances has been deployed sucessfully:
dcos marathon app list -
Verify the Apache® Mesos® task relevant to services and the pool instances:
dcos task list -
Verify that the Edge-LB pool named
nginx-edgelbdeployed successfully:dcos edgelb list -
Verify that the Edge-LB pool instance deployed successfully with the configured frontend and backend ports:
dcos edgelb endpoints nginx-edgelb
Verify service access
-
Access the
nginx-mlbservice using the public IP address and port specified in thenginx-mlb.jsonfile.http://<public_agent_public_IP>:10020You should see a page for
Welcome to Nginx - through Marathon-LB. For example: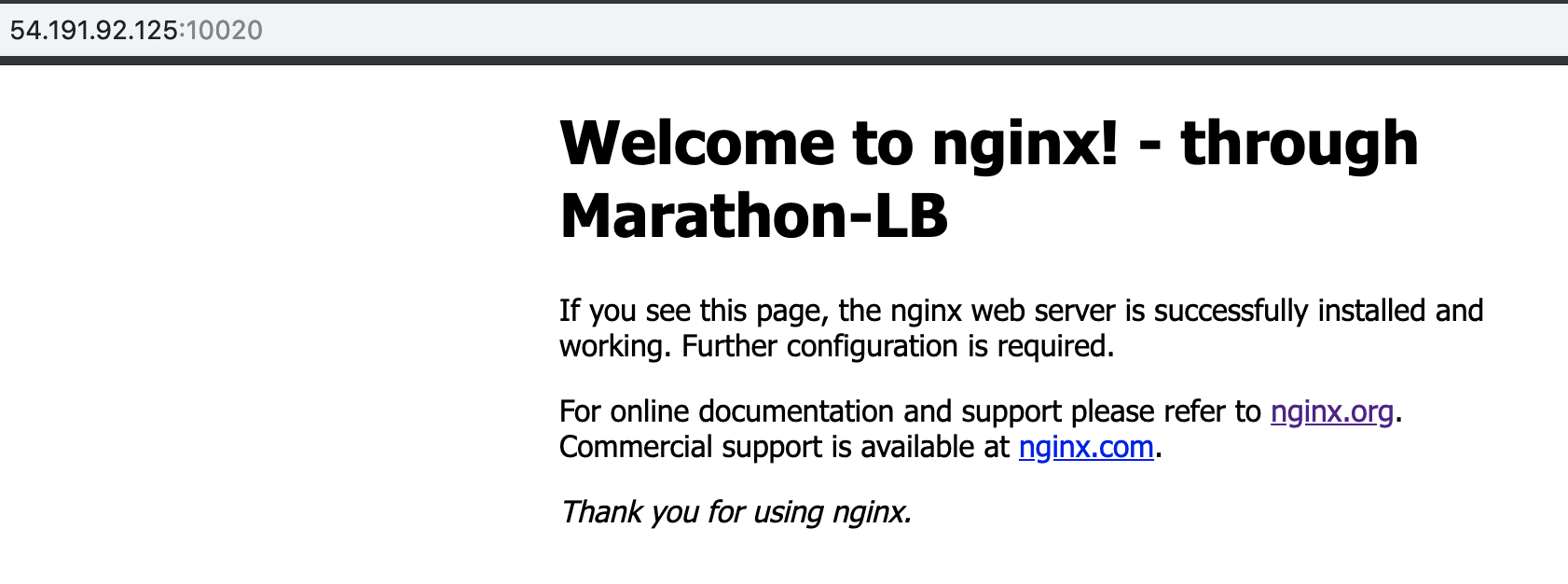
-
View the load balancing statistics for the
nginxservice deployed using Marathon-LB using the default HAProxystatsport 9090:http://<public_agent_public_IP>:9090For example:
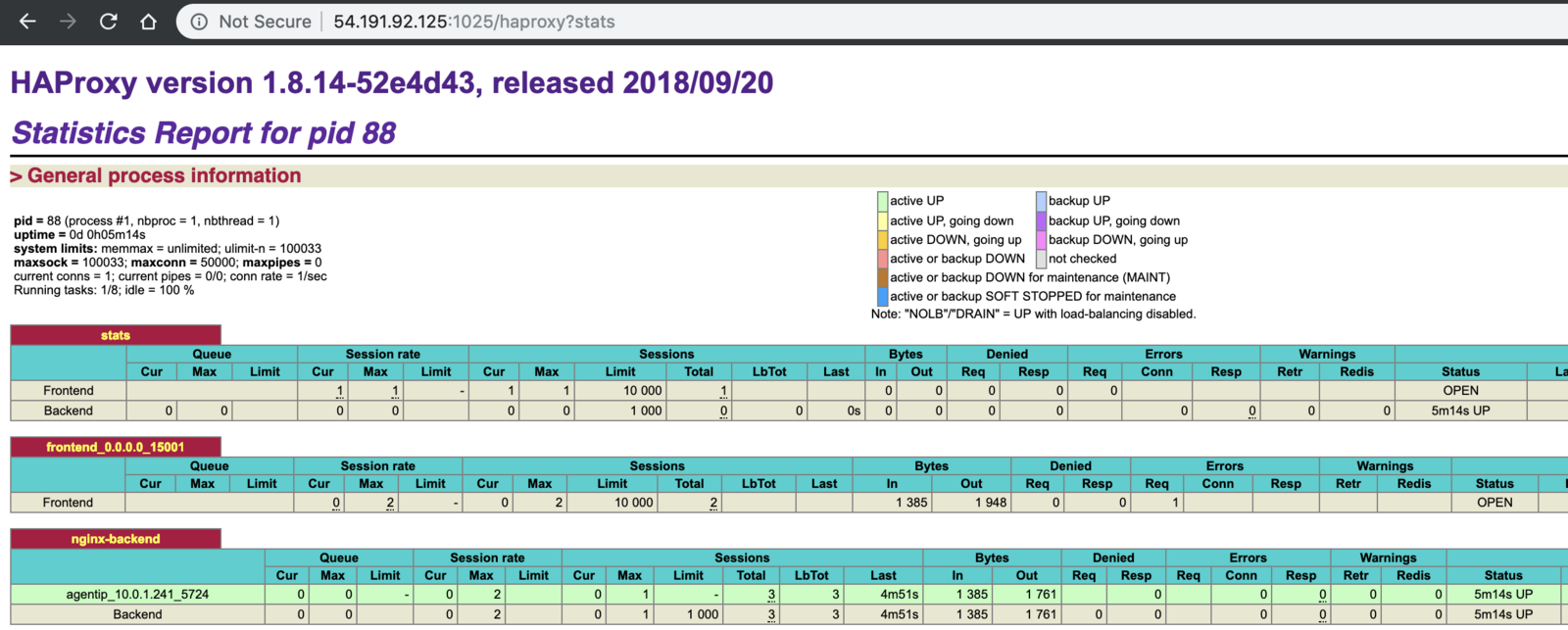
-
Access the
nginxservice that was exposed through Edge-LB using the public agent IP and the frontend port number.http://<public_agent_public_IP>:15001You should see a page for
Welcome to Nginx - through Edge-LB. For example: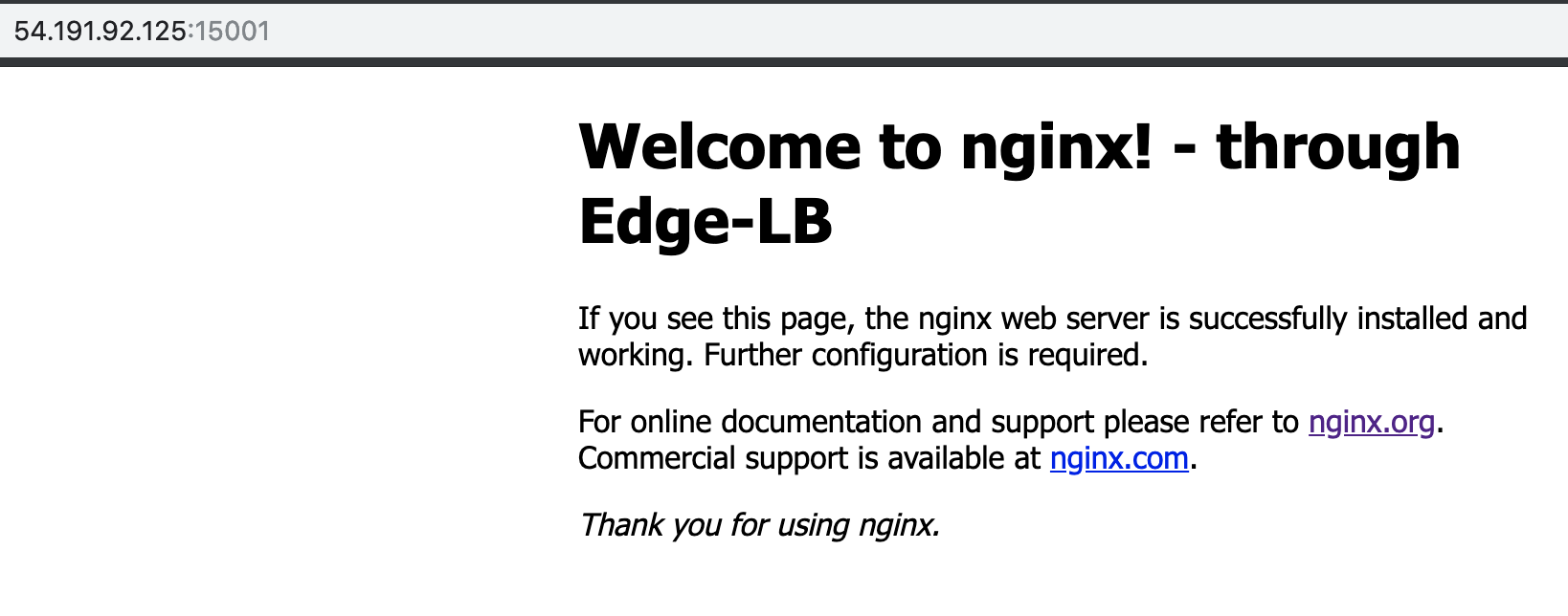
-
View the load balancing statistics for the
nginxservice deployed using Edge-LB using the predefined HAProxystatsport 1025:http://<public_agent_public_IP>:1025For example:
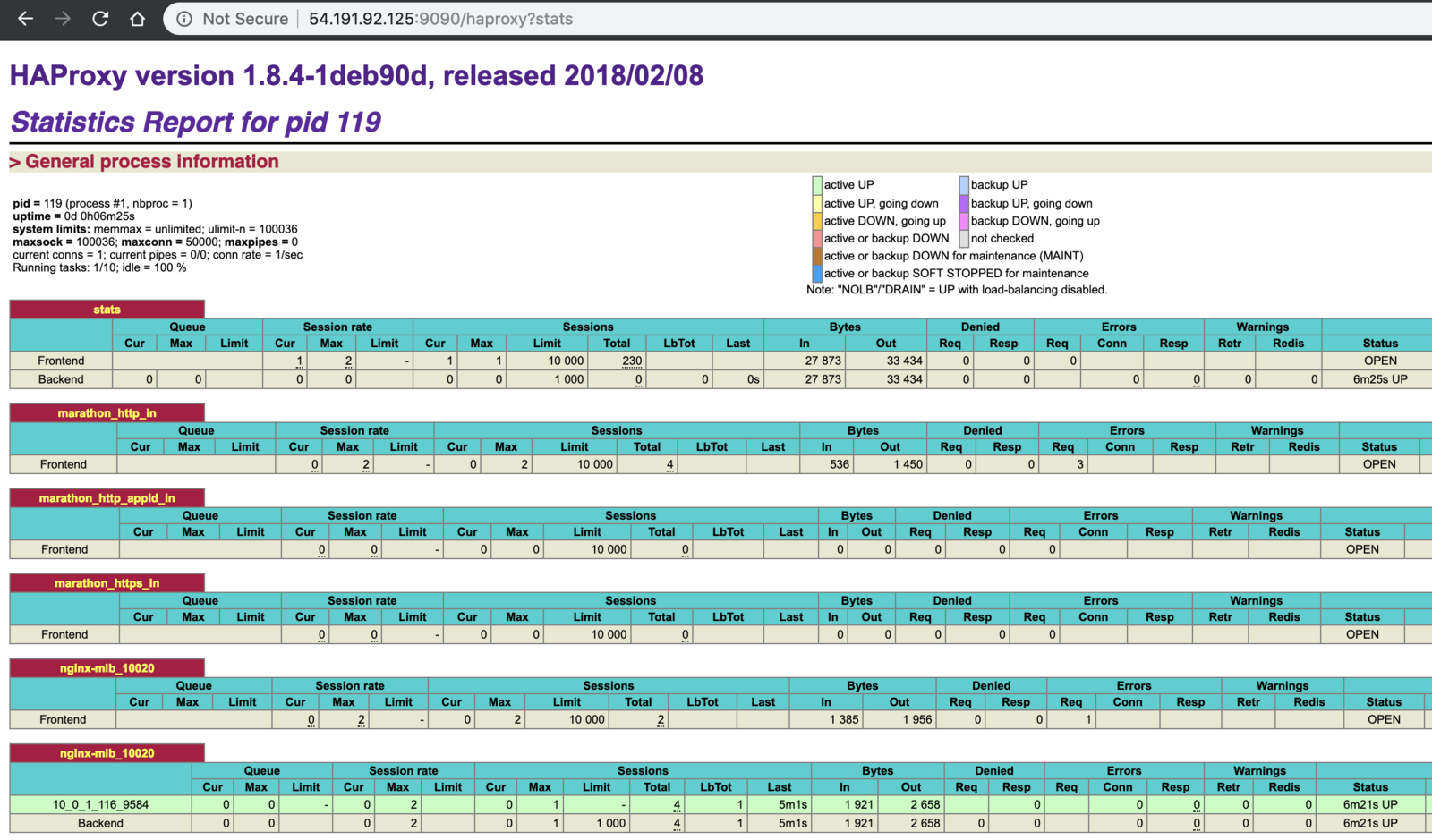
 Edge Lb Documentation
Edge Lb Documentation