Edge-LB is designed to handle load balancing and proxying for a distributed architecture. It is usually deployed on the public agent nodes of a cluster so that the services running on the cluster remain protected inside of a security perimeter. The public agent nodes are typically in demilitarized zones (DMZs) or in perimeter external networks that are outside of the DC/OS cluster and your organizational WAN, LAN, or VPN networks.
In general, you should deploy Edge-LB on multiple public nodes to support high availability for traffic entering the cluster.
Key Edge-LB components
Edge-LB relies on the following core components to provide proxy and load-balancing service for inbound traffic to the DC/OS cluster:
- Edge-LB API server
- Edge-LB pool
- Individual load balancer
Edge-LB API server
The Edge API server enables you to create, modify, and delete Edge-LB pools and their associated pool configuration settings. Essentially, the Edge-LB API server provides load balancing orchestration service for traffic entering the cluster.
The Edge-LB API server:
- Performs create, read, update, and delete (CRUD) actions on Edge-LB pool(s).
- Responds to Edge-LB pool-related API endpoint queries.
- Stores the pool configuration in a configuration management system and automatically updates and reloads pool configuration changes.
Edge-LB pool
While the Edge-LB API server is responsible for creating, deleting, and updating Edge-LB pool instances, Edge-LB pools handle the main load balancing and proxying tasks for the cluster. Because each Edge-LB pool has a corresponding pool configuration file, it is the pool configuration settings that control how requests are authenticated and routed to specific backend nodes and ports.
Individual load balancers
Using the configuration settings defined in the pool configuration file, Edge-LB pool instances receive, then distribute inbound traffic to individual load balancers. To handle discrete, lower-level load balancing tasks, Edge-LB pools leverage built-in features from the HAProxy load balancer. When the Edge-LB API server launches an Edge-LB pool, the Edge-LB pool launches one or more HAProxy instances inside the pool instance to complete the load balancing process and deliver the request to proper backend.
Basic workflow
The basic workflow summary for Edge-LB operations is:
- Deploy a service on DC/OS cluster.
- Install the Edge-LB packages on the cluster.
- Create an Edge-LB pool instance to expose the service externally.
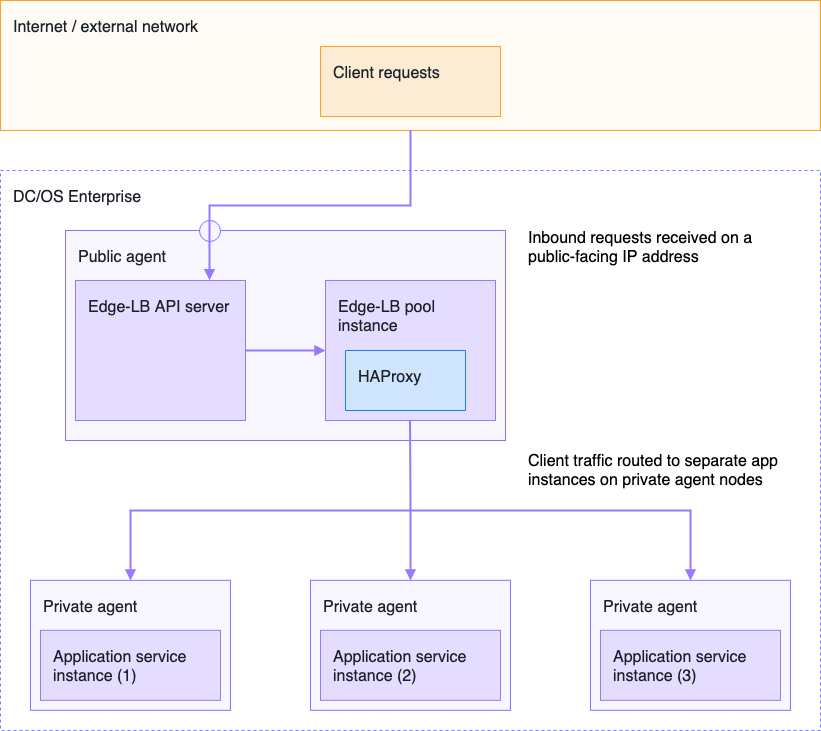
After the service is exposed on the public agent node, clients can request access to the service. The Edge-LB API server listens for these requests, and orchestrates how the requests are distributed to new or existing Edge-LB pools. The pool instance then manages load balancing of the incoming requests and distributes traffic to individual load balancers (HAProxy processes) so that requests are delivered to the appropriate backends.
As a cluster administrator, you can deploy Edge-LB pools to handle specific tenants, geographic locations, or types of applications.
The following diagram provides a simplified architectural view of Edge-LB:
 Edge Lb Documentation
Edge Lb Documentation