Service accounts are used in conjunction with public-private key pairs, secrets, permissions, and authentication tokens to provide access for DC/OS services to DC/OS. Service accounts control the communications and DC/OS API actions that the services are permitted to make.
DC/OS services require authentication depending on your security mode.
| Security mode | Intracluster communication | External cluster communication |
|---|---|---|
| Permissive | Optional | Required |
| Strict | Required | Required |
Service Authentication Components
To authenticate a service, you will need:
- Public-private key pair
- Service account
- Secret for service account
- Permissions for service account
- Service login token
JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
Service authentication involves two JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for service authentication.
-
Service Login token To log in to DC/OS, a service login token is required. This is a JWT signed with the service’s private key, and serves as a one-time password. A service login token should be generated for one-time usage (for example, for a single service login procedure) and should include an expiration.
-
Authentication token After a service connects to DC/OS with the service login token, the IAM service creates an authentication token which the service can then use to authenticate its outgoing requests to DC/OS. An authentication token can be used for long-term access.
Mesos Authentication Principal
DC/OS services supply a principal when they register with the Mesos masters. In strict security mode, the service account name must match the name specified in the principal. For more information about principals, see the Mesos documentation.
The following diagram illustrates this sequence.
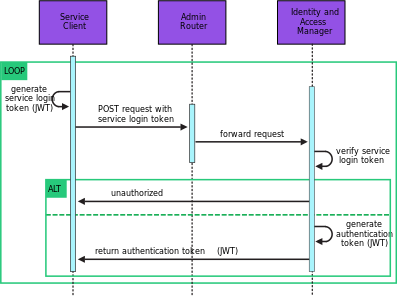
Figure 1. Service authentication
 DC/OS Documentation
DC/OS Documentation